Comparison between Three-Lobe Roots Blowers VS Two-Lobe Roots Blowers
1. Roots blowers Differences in Impeller Structure and Operating Principle.
- Two-Lobe Type: Utilizes two impellers (blades), dividing the effective volume of the blower chamber into two equal parts. This results in significant airflow pulsation during operation, resulting in high outlet noise and poor operational stability.
- Three-Lobe Type: Utilizes three impellers spaced 120° apart, dividing the effective volume into three equal parts. This reduces the Holm resonance effect, significantly improves airflow pulsation, and reduces vibration and noise by over 20 decibels.
-
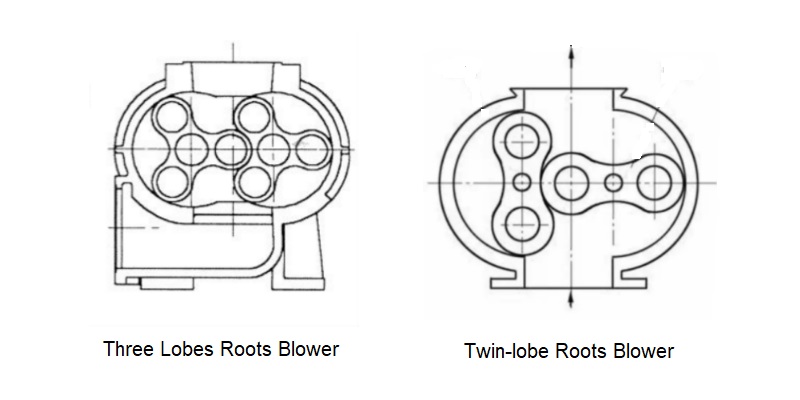
Structure Comparison between three lobes roots blower and twin-lobe roots blower
Structural differences directly affect the continuity of airflow and sealing efficiency. The three-blade rotor has a stronger barrier effect on leaking gas and can maintain air pressure stability in a higher pressure chamber.
- Performance comparison and efficiency differences
| Compared items | Three-Lobe Roots Blowers | Two-Lobe Roots Blowers |
| Vibration&Noise | Low (high exhaust frequency, small pulsation) | Higher (obvious airflow pulsation) |
| Bearing Service Life | Extended by about 15% (better mechanical properties) | Relatively short |
| Displacement & Pressure | Larger displacement and wider pressure range (up to 196kPa) for the same size | Low displacement, suitable for medium and low pressure scenarios (<100kPa) |
| Energy consumption and efficiency | More energy-saving (small internal leakage flow) | High energy consumption and relatively low efficiency |
| The three-lobe design improves gas delivery efficiency and mechanical stability through precise gap control (smaller gap between impeller and casing) |
3. Application Scenarios and Economic Efficiency
- Three-lobe roots blowers are primarily used in applications requiring low noise and high stability, such as sewage treatment aeration, pneumatic conveying, and chemical refining. Advantages include a long maintenance cycle (e.g., extended lifespan of Vitonoil seals) and a lower overall cost.
- Two-lobe roots blowers are suitable for conveying high-flow gases such as coal gas, natural gas, or sulfur dioxide. While their structure is simple, they require additional noise control investment. Smaller models have been largely replaced by three-lobe blowers.
- In high-pressure or space-constrained environments, three-lobe blowers are preferred due to their compact design and low vibration characteristics

